Earliest Date and Overdue Date
As of version 1.11.1, ICE has offered the option of returning the Earliest Date and Overdue Date as a part of the forecast, along with the Recommendation Date.
The Earliest Date and Overdue Date are defined as follows:
- The Earliest Date is the soonest date that the vaccine can be administered and still be considered valid, not counting the usual 4-day grace period. The earliest date may be useful in cases where, for example, a child is in the office for an appointment and is not yet due for a particular vaccine, but the clinician wants to know if it would be acceptable to administer it early. It's generally recommended to administer vaccines when they are recommended and not sooner, unless the patient has special risk factors.
- The Overdue Date is the date after which an immunization administered would be considered late.
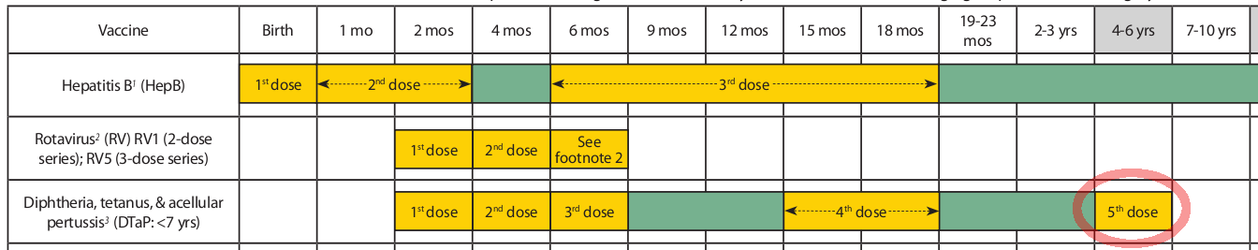
As an example, the 5th dose of DTaP is recommended at 4-6 years, as circled in red below. That is, for a typical child, the recommended due date for dose 5 of DTaP is the date of the child's 4th birthday. The overdue date would be the date of the child's 7th birthday.
Clinicians may or may not be interested in overdue date. The overdue date could be used to present an alert that a vaccine recommendation is already overdue. In an EHR, for example, the display might highlight a forecast in red if today's date is on or after the overdue date.
As noted above, the general advice is to administer a vaccine as soon as of the ICE Recommendation Date. For this reason, not everyone may wish to use the Overdue Date feature.
For more information on how to incorporate these new dates into your installation of ICE, please refer to the ICE Implementation Guide or contact the ICE team at ice@hln.com.